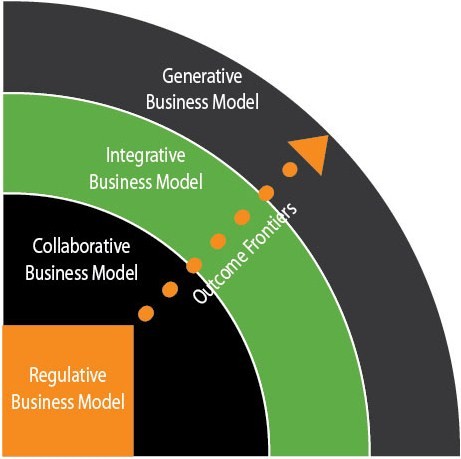
With an Integrative Business Model, the focus broadens to complete integration of multiple programs and services in order to improve customer service, increase participation, and support data-driven policy and decision making. In addition, the mission and operating model of the organization is supporting a shift to whole-person and family centric service design. Strategically and operationally, the enterprise bolsters family centric outcomes through seamless, cross-boundary collaboration. Information technologies support enterprise-wide back-office processes, as well as front-office innovations such as individualized client services focused on self-sufficiency, improved health outcomes, and social inclusion.
Diagnostic Metrics & Checkpoints:
- Outcomes & Impact Design: The enterprise is activating an outcomes model that connects desired impact to overall community priorities and expands the focus to include cross-agency outcomes, metrics, and real-time situational awareness.
- Organizational & Practice Design: The enterprise is establishing new governance structures, management and operating processes, and data and analytics that focus on and help employees support and drive customer-focused outcome goals.
- Systems & Technology Design: The enterprise is implementing an integrated, single-view system for case management across programs and organizations and enabling service collaboration and outcome tracking by customer and by aggregate.
Look to the State of Ohio, New York City and Spain for prime examples of the move to an Integrative Business Model. In all three places human services systems faced similar challenges - skyrocketing demand and spending, silo-based services, and cumbersome technology – all of which led to suboptimal outcomes and value.
In Ohio the Office of Health Transformation was established to oversee strategic planning and budgets on key initiatives including modernizing Medicaid, streamlining health and human services, and engaging non-profit and private sector partners. A key strategy was integrating state and local silos into an 11-agency Health and Human Services Cabinet that publishes an integrative health budget. As a result, an outcomes-oriented mission has taken hold, with local health districts utilizing shared services and creating health plans by region, officials utilizing data and analytics to shape policy, and sectors working together to track performance measures.
Spain has moved to increase human services collaboration and integration in order to respond to the surge in demands from the lingering financial crisis. The reform plan touches the entirety of public administration, and brings forward a new vision and model for the Spanish welfare system – one that is more integrated and efficient, more sustainable and outcomes-oriented, and more responsive to citizen needs. Spain’s strategies include increasing coordination and integration across all administrative levels to reduce duplicities, using analytics and technology to evaluate public policies, and squeezing savings out of the integration of health and welfare services. Since 2008, Spain’s efforts have saved more than $21 billion (Euros).
For their move to integration, New York City health and human services (HHS) officials focused on performance management and data analytics by launching HHS Connect, a system integrating 35 programs across 15 agencies. A new outcomes model represents HHS Connect priorities, impacted client groups, and outcomes, and is used for every HHS initiative. Today, each initiative must pay for itself through measurable outcomes and metrics such as savings, reduced headcount, or greater productivity. In addition, citizens get a one-stop online shop for multiple program eligibility and online benefits access, and a worker portal allows staff to see metrics and analysis across agencies.